 Banking Customer Data Breach Case in Southeast Asia
Banking Customer Data Breach Case in Southeast Asia What Caused Banking Customer Data Breaches
What Caused Banking Customer Data Breaches Challenges for Customer Data Loss Prevention in Banking
Challenges for Customer Data Loss Prevention in Banking How CyberServal Protects Sensitive Data for Banking
How CyberServal Protects Sensitive Data for Banking Case Preview: How to Close the " Invisible Exit" of Outsourced Data
Case Preview: How to Close the " Invisible Exit" of Outsourced Data
How Banks Stay Ahead of Data Breach Risks in Security Planning?
Banking Customer Data Breach Case in Southeast Asia
As digital transformation accelerates, banks in Singapore, Malaysia, and across Southeast Asia face increasingly complex challenges in data security. One of the most critical risks is customer information leakage, which can cause lasting reputational damage and regulatory consequences.
In July 2025, PT Bank Perkreditan Rakyat Serang in Indonesia experienced a severe breach where sensitive customer and loan information was stolen and posted for sale on an underground forum. This incident highlights how financial institutions, particularly smaller or regional banks with weaker security infrastructures, are often prime targets for cybercriminals.
Banks must prioritize robust database protection, implement advanced intrusion detection systems, and maintain constant vigilance against leakage risks. Proactive monitoring, rapid response capabilities, and adherence to international compliance standards are no longer optional but essential for safeguarding customer trust and ensuring business continuity in today’s digital banking landscape.
What Caused Banking Customer Data Breaches
External hacking remains one of the most significant threats to the banking sector, particularly as cybercriminals increasingly exploit AI-driven tools to launch faster and more sophisticated attacks. However, not all breaches originate from external actors. In many cases, risks arise within business departments that rely heavily on outsourcing.
Outsourced personnel often use computers that interact with both internal banking systems and external internet resources, creating potential vulnerabilities. Sensitive data may also be leaked through everyday tools such as USB flash drives or informal channels like WhatsApp and LINE, making insider-related risks equally critical to address.
Challenges for Customer Data Loss Prevention in Banking
Traditional Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools were designed years ago, but today’s banking environment has changed dramatically. When it comes to preventing customer information leakage, comparing with next-gen data loss prevention products, these older systems show several weaknesses.
Limited Content Matching. Traditional DLP mainly relies on content matching methods such as keywords, regular expressions, and file fingerprints. While this works for straightforward text, it struggles to detect sensitive data hidden in compressed files, encrypted formats, or even slightly modified content. This leaves dangerous gaps that attackers or careless insiders can exploit.
Blind Spots in Multi-Cloud and Mobile Environments. Employees work across different platforms, often accessing data from cloud services and mobile devices. Traditional DLP cannot provide full visibility or control across these diverse systems. As a result, sensitive customer data can still be copied, transferred, or uploaded to the cloud without effective blocking.
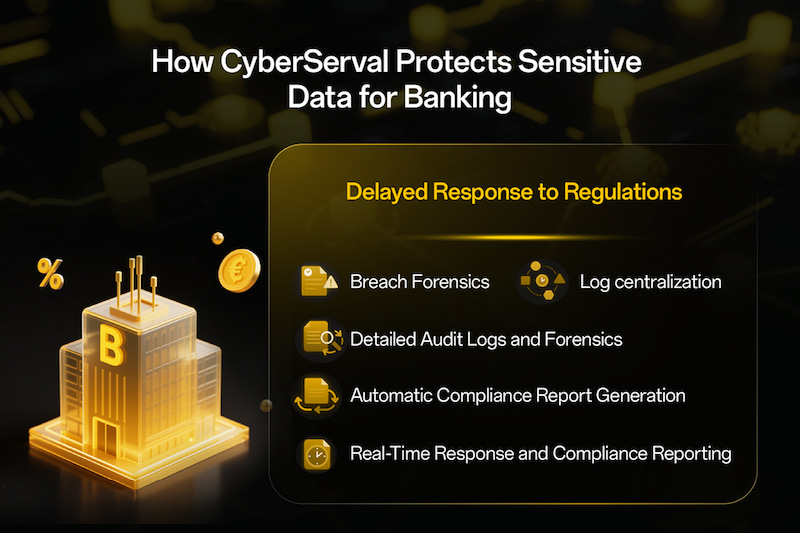
Delayed Response to Regulations. Regulatory compliance is another big challenge. Authorities like MAS in Singapore or BNM in Malaysia require fast and accurate reporting when a data leak occurs. But with traditional DLP, logs are often scattered across different systems, making it slow and difficult to reconstruct the scope and impact of the breach. This delays response and increases compliance risk.
How CyberServal Protects Sensitive Data for Banking
1. DDR Security Solutions for Limited Content Matching
AI-Enhanced Detection and Semantic Understanding: Leveraging an AI content insights engine enhanced by LLMs (Large Language Models), CyberServal DLP company provides a deep understanding of the semantics of unstructured data, accurately identifying sensitive information and specific data patterns even without explicit keywords. This is advantageous over traditional keyword-based or regular expression-based content recognition methods.
Data lineage: DDR identifies important data by tracking the data lineage, understanding the source of the data, the flow path, and how it is processed. This allows data to be traced and protected by its type and ancestry information, even if it is encrypted or compressed.
Anti-Adversarial Capabilities: DDR can detect various covert behaviors, such as obfuscation techniques such as file copying, compression, and renaming, ensuring that data is not easily tampered with before being leaked.
Multi-dimensional file analysis: DDR analyzes files through multiple dimensions such as file format, encoding, and fingerprint, accurately identifying sensitive data.

2. DDR Security Solutions for Blind Spots in Multi-Cloud and Mobile Environments
Full platform compatibility: DDR clients are well adapted to mainstream operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux, and support domestic Xinchuang operating systems such as Kirin and UnionTech.
Unified Cloud and Endpoint Control: DDR provides unified control over cloud platforms, end devices, and SaaS applications. It connects to authorized cloud applications like Office 365 and Google Workspace through cloud API connectors to gain visibility into content created and shared in the cloud.
Browser Extensions and Endpoint Agents: DDR deploys lightweight endpoint agents and browser extensions to comprehensively monitor network behavior and web-based cloud application telemetry data across all major browsers, covering data and users that traditional cybersecurity tools might overlook.
Comprehensive monitoring of outgoing channels: DDR provides comprehensive monitoring of all outgoing transmission channels on the endpoint, including USB devices, instant messaging applications (IM), web applications (browsers), LAN sharing, network protocols (such as Git, SVN, AirDrop, RDP, SMB, FTP, SCP, screen sharing), and hardware devices (such as optical drives, printers, Bluetooth) to ensure that sensitive data transmission is restricted or blocked.

3. DDR Security Solutions for Delayed Response to Regulations
Real-Time Response and Compliance Reporting: DDR provides real-time incident response and compliance reporting capabilities. It can track the entire chain of data flow, from data download and local processing to outgoing transmission, no matter how the data is transmitted, modified or converted, it can be accurately captured and recorded, so as to clearly show the data flow direction and help managers more accurately identify and deal with potential data leakage risks.
Detailed Audit Logs and Forensics: DDR provides detailed reporting and audit trail capabilities, allowing banks to maintain a complete record of data access, usage, and compliance activities, facilitating internal audits and demonstrating compliance to external auditors and regulators.
Breach Forensics: DDR supports incident screenshots and screen recordings (10-second video before and after the incident) to gather evidence of the breach and help reconstruct the incident.
Log centralization: Data leakage risk logs can be delivered to the Kafka server and aggregated with logs from other platforms for convenient operation and maintenance analysis.
Automatic Compliance Report Generation: DDR supports the generation of compliance reports such as PCI-DSS, GDPR, and etc.
Case Preview: How to Close the " Invisible Exit" of Outsourced Data
In outsourced banking departments, contractors often work between internal systems and external networks, handling significant amounts of data. Due to the nature of the role, sensitive information may flow out through common channels such as external drives or instant messaging apps—posing major regulatory and compliance challenges.
✍️How a Prominent Bank Secures Sensitive Data and Simplifies Audits with DDR
👉 For more detailed data loss prevention technologies, you can download our latest DLP whitepaper.
In our upcoming case study, we’ll demonstrate how to tackle this issue while ensuring smooth operations and protecting customer data. Subscribe to receive more insights.